Life expectancy has risen remarkably and the number of older people will continue to increase. Aging is a major risk factor for neurodegenerative diseases that involve protein aggregation, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Huntington’s (HD), Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. We have discovered that aging induces a rewiring of the ubiquitinated proteome, whereby hundreds of proteins undergo changes in ubiquitin modifications. Given the central role of ubiquitination in cell function, a functional study of these alterations can lead to novel modifiers of aging and disease. Together, our approach that combines state-of-the-art proteomics, human iPSC-disease modelling and genetics in the model organism C. elegans can provide insights into converging strategies for preventing and/or treating different age-related neurodegenerative disorders.
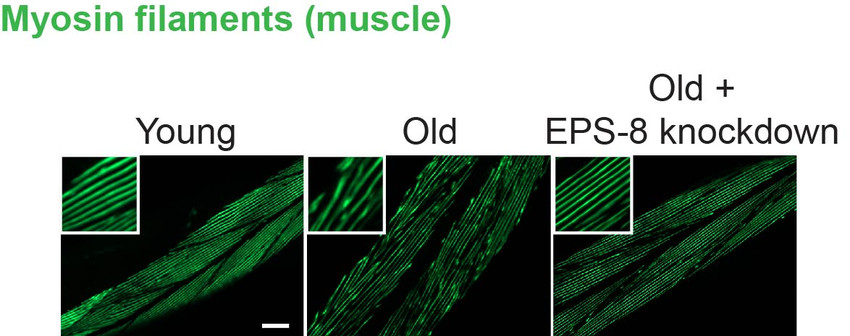
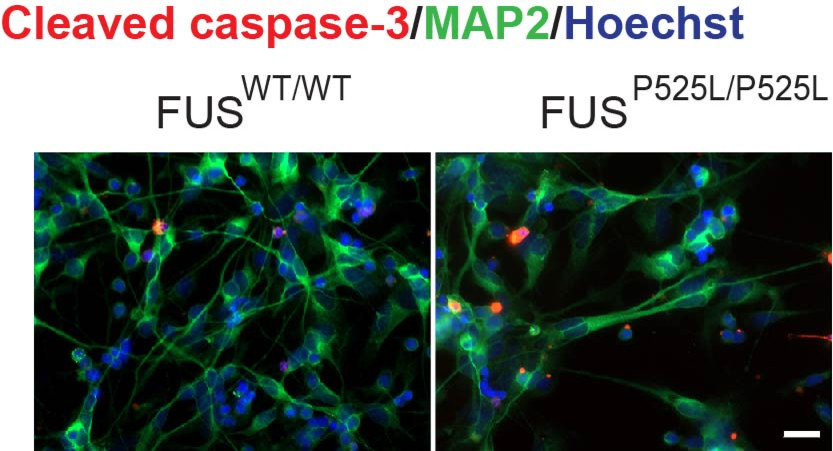
Aging causes a progressive loss of physiological integrity, which can trigger the development of multiple pathologies that remain incurable. As such, our ever-aging society presents a challenge from the increasing prevalence of age-related diseases. Our innovative approach will define targets to slow down aging and prevent age-related neurodegenerative diseases. Thus, our project can have important implications for multi-disease prevention and be of enormous benefit for our ever-aging society.

CECAD Research Center
CMMC - PI - C 16
show more…+49 221 478 84172
CECAD Research Center
Joseph-Stelzmann-Str. 26
50931 Cologne
Postdocs
Seda Koyuncu, Hyun Ju Lee, Will Zhang
PhD students
Hafiza Alirzayeva, Saygin Bilican, Franziska Hommen, Angela Joy Johns, Markus Wehrmann
Master student
Yara Nabawi
Technicians
Melissa Chmara, Nassima Salarzai