Sufficient tissue oxygenation critically contributes to tissue homeostasis. Moreover, oxygen is an important substrate for antimicrobial effector enzymes such as the inducible (type 2) nitric (NO) synthase or the phagocyte oxidase.
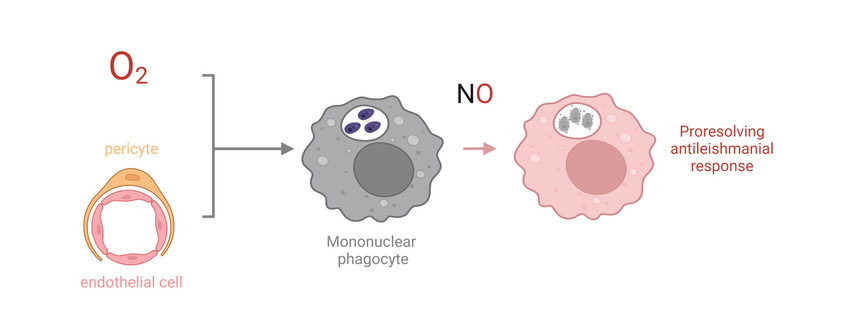
We use a murine model of cutaneous leishmaniasis to address the bidirectional interplay of tissue oxygenation and antimicrobial control. We have revealed that Leishmania skin lesions display low oxygen levels and that macrophages activated under these oxygen tensions fail to produce sufficient amounts of leishmanicidal NO to clear Leishmania. Resolution of disease requires normalization of lesional tissue oxygenation which is linked to enhanced tissue perfusion. In this project we would like to assess the contribution of pericytes and endothelial cells in normalizing tissue oxygenation and in resolution of disease.
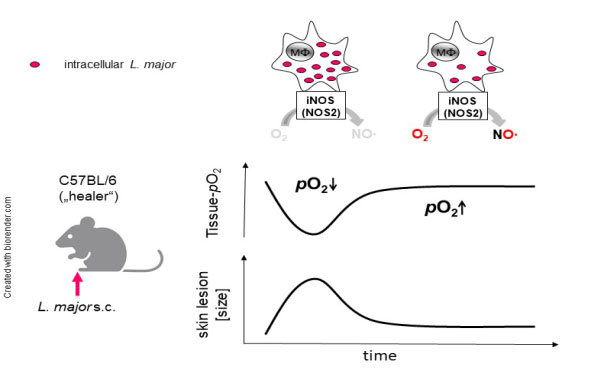
Leishmaniasis belongs to the neglected tropical diseases. It is a chronic and notoriously difficult to treat disease. In this proposal we aim to identify new adjunctive therapeutic vascular targets for the treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis. Moreover, these findings will shed new light on the bidirectional immunovascular crosstalk in infectious disease in general and might be useful for treating other (chronic) infections and inflammatory conditions as well.
References:
Mougneau et al., Immunol Rev, 2011, 240, 286-296
Jantsch et al., 2015, Immunobiology, 220, 305-314
Hayek et al., 2020, Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 78, 1887-1907
Mahnke et al., 2014, J Invest Dermatol, 134, 2339-2346
Frick et al, 2022, Front Immunol, 13:789366

Institute for Medical Microbiology, Immunology and Hygiene
CMMC - PI - B 05
jonathan.jantsch[at]uk-koeln.de
show more…+49 0221 478 32000
Institute for Medical Microbiology, Immunology and Hygiene
Goldenfelsstraße 19-21
50935 Cologne