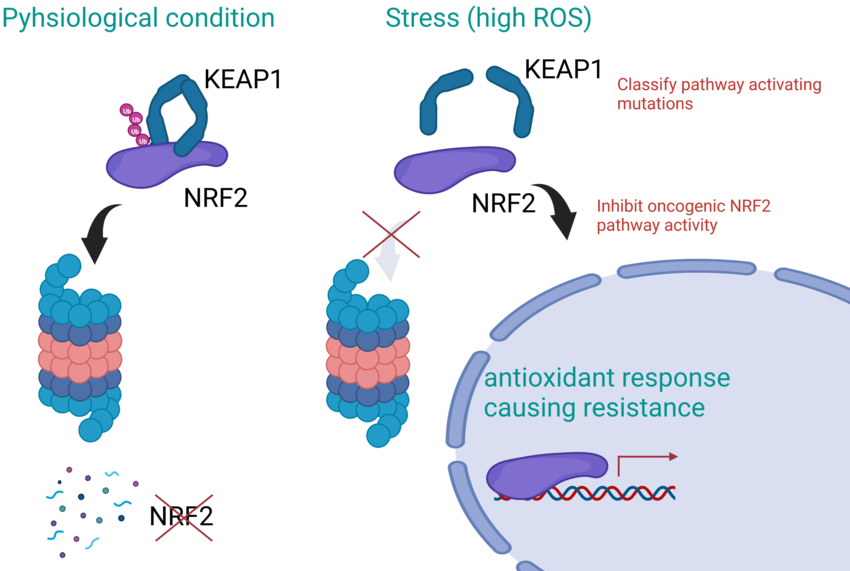
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death with lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) as the most frequent subtype. KEAP1 is mutated in 15-20% of LUAD, a patient group with particularly poor prognosis. In situations of high reactive oxygen species (ROS), NRF2 initiates the expression of pro-survival genes that quench ROS. In KEAP1 mutated LUAD, the NRF2 pathway is constitutively active, allowing the cancer to cope with high ROS levels. This adaptation makes cancer cells resistant to radio- and chemotherapy. There is an urgent clinical need to develop new treatment strategies for patients with KEAP1 mutated LUAD. A promising strategy is to inhibit the NRF2 pathway. In the proposed project, we will evaluate the pathogenic role of individual KEAP1 mutations by screening our clinical cohort using immunohistochemistry and our recently developed expression assay that identifies tumors with NRF2 pathway activity. In addition, we will test for the functional consequences of specific KEAP1 mutations in vitro. Further, we will search for genomic alterations other than KEAP1/NFE2L2 mutations that can activate the NRF2 pathway. Finally, we will establish model LUAD cell lines with inducible KEAP1 activity to screen drugs with effects specific for KEAP1 mutated tumors. The effect of candidate drugs will be further characterized by proteomics and metabolomics. Overall, we will pave the way to new treatment strategies for a large group of LUAD patients with poor prognosis.

Institute for General Pathology and Pathological Anatomy
CMMC - PI - A 06
show more…
+49 221 478 85643
Institute for General Pathology and Pathological Anatomy
Joseph-Stelzmann-Str. 26
50931 Cologne
https://pathologie.uk-koeln.de/forschung/genomische-pathologie-ag-hillmer/

Institute for General Pathology and Pathological Anatomy
CMMC - PI - A 03
CMMC - Co-PI - A 06
Executive Board Member
reinhard.buettner[at]uk-koeln.de
show more…+49 221 478 6320
+49 221 478 6360
Institute for General Pathology and Pathological Anatomy
Kerpener Str. 62
50937 Cologne
PostDocs
Christina Ali Dousty Shahraki
Sascha Hoppe
Sonja Meemboor
Sebastian Michels
Ali Yazbeck
PhD students
Mohammad Ali (Shahrokh) Karimpour
Christoph Jonas
Marta Pistone
Master student
Minkyung (Rachel) Beak
Medical students
Marten Wenzel
Patrizia Pauls
Technicians
Barbara Holz
Vanessa Richartz
Visiting scientist
Antonio Ungaro